介紹完堆疊之後,今天要來介紹佇列(Queue),會集中討論 Queue 的實作方法。
佇列就是指:一個具有先進先出(First-In First-Out, FIFO)性質的有序串列。從 Queue 的底端(rear)加入元素,從 Queue 的前端(front)取出元素。
大家可以想像,日常生活中的排隊情況,佇列就像是一個隊伍一樣,先進入的會在排頭(front),後進入的會在排尾(rear)。
佇列一樣有 2 種實作方式,Array 和 Linked List。今天會先看 Array 的部分
用個簡單的示意圖來講解一下 enqueue 和 dequeue 以及這個 linear array 會有的問題: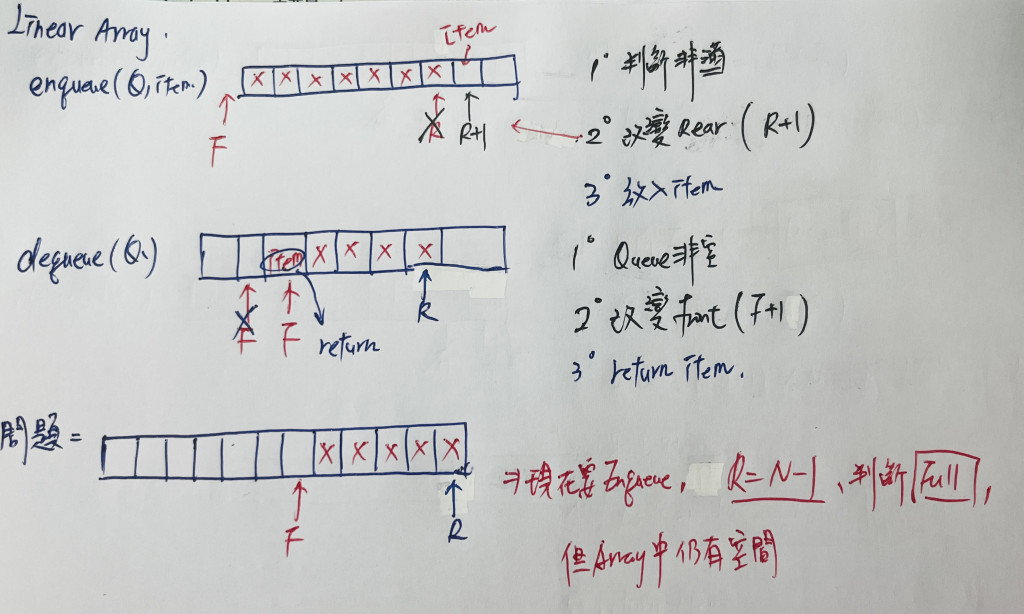
可以看到,明明 Array 中都還有空間,但是已經判定滿了?問題在於陣列已使用過的空間不能重複使用。
直覺來說,當 rear = N - 1 時,可以將所有元素往前搬,但因此會導致需要使用迴圈,原本 O(1) 的動作將會變成 O(n),花費了更多時間。
以此,為了解決這種狀況,有了第二種方法:Circular Array
Circular Array 的重點就是 取餘數運算(mod, %),當使用到陣列最後一個空間,可以透過 % 運算回到陣列第一個空間使用。例如:Rear 在 位置 N - 1 格,enqueue 時 (rear + 1) % N = N % N = 0,會回到陣列第0個位置。
0. 先準備一個大小為 N 的陣列當作佇列,再來準備兩個整數 Index:front、rear。rear 代表目前尾端之0位置,front代表前端之前一個元素位置。
用個簡單的示意圖來講解一下 enqueue 和 dequeue 以及這個 Circular array 會有的問題: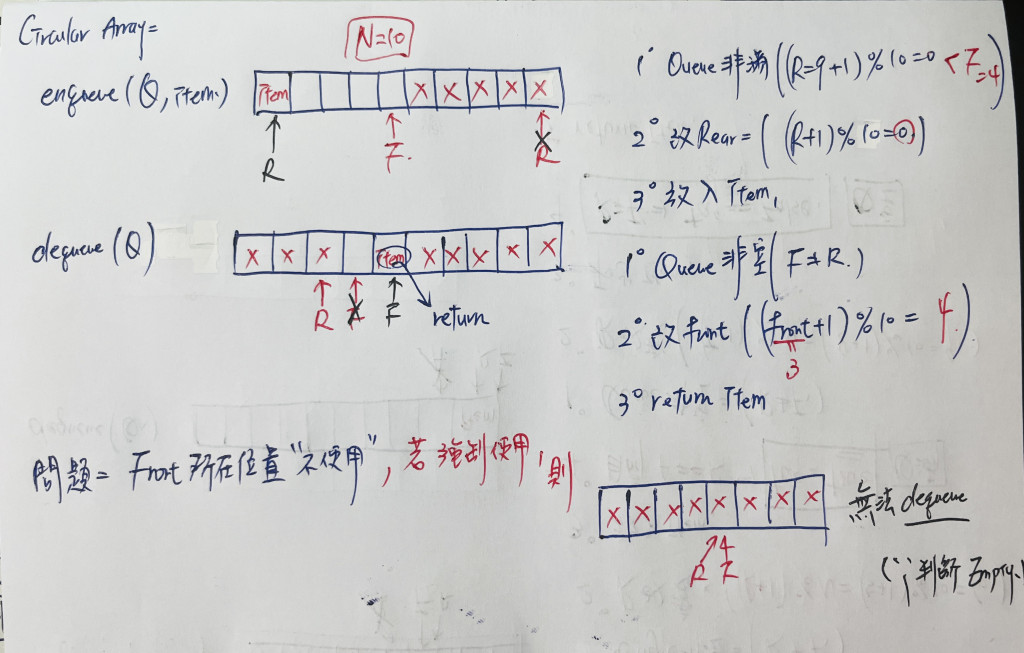
我們可以發現,front 所在位置是不放元素的,如果執意要放,這時候 Rear 和 front 會出現在同一格,因此無法 dequeue,因為 dequeue 會判斷佇列為空,但其實佇列是滿的。因此此種寫法只能使用 N - 1 格。
這個問題的根本原因,是因為判斷空和滿的條件是一樣(都是 front == rear),所以,新增一個變數 tag 來判斷空或滿。
老樣子,來個示意圖: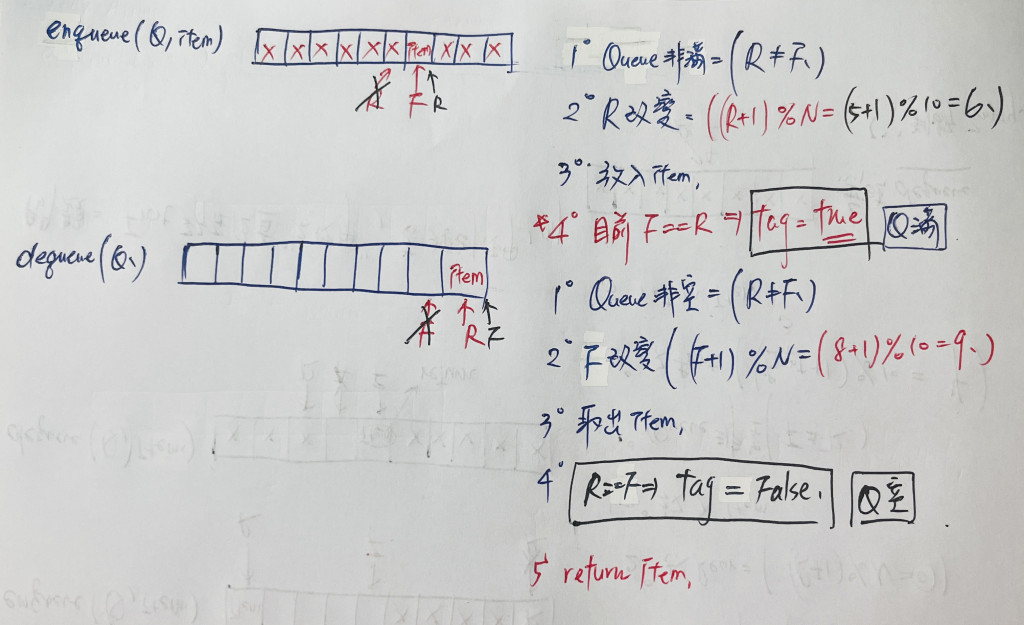
雖然使用了 N 個空間,但多花了一個判斷式的時間以及多一個變數,實務上還是會用第二種方式較多喔!
#include <iostream>
#include <limits.h>
#define SIZE 256
using namespace std;
class Queue{
// Circular Array use (N - 1) space Implementation
private:
int* arr;
int front, rear;
public:
Queue();
bool isEmpty();
bool isFull();
void enqueue(int item);
int dequeue();
};
Queue::Queue(){
this->arr = new int[SIZE];
this->front = 0;
this->rear = 0;
}
bool Queue::isEmpty(){
if(this->rear == this->front) return true;
else return false;
}
bool Queue::isFull(){
int temp = (this->rear + 1) % SIZE;
if(temp == front) return true;
else return false;
}
void Queue::enqueue(int item){
if(isFull()){
cout << "enqueue fail." << endl;
}else{
this->rear = (this->rear + 1) % SIZE;
arr[this->rear] = item;
}
}
int Queue::dequeue(){
if(isEmpty()){
cout << "dequeue fail." << endl;
return INT_MIN;
}else{
int x = arr[this->front];
this->front = (this->front + 1) % SIZE;
return x;
}
}
#include <iostream>
#include <limits.h>
#define SIZE 256
using namespace std;
class Queue{
// Circular Array use N space Implementation
private:
int* arr;
int front, rear;
bool tag;
public:
Queue();
bool isEmpty();
bool isFull();
void enqueue(int item);
int dequeue();
};
Queue::Queue(){
this->arr = new int[SIZE];
this->front = 0;
this->rear = 0;
this->tag = false;
}
bool Queue::isEmpty(){
if(this->rear == this->front && !(this->tag)) return true;
else return false;
}
bool Queue::isFull(){
if(this->rear == this->front && this->tag) return true;
else return false;
}
void Queue::enqueue(int item){
if(isFull()){
cout << "enqueue fail." << endl;
}else{
this->rear = (this->rear + 1) % SIZE;
arr[this->rear] = item;
if(this->rear == this->front) tag = true;
}
}
int Queue::dequeue(){
if(isEmpty()){
cout << "dequeue fail." << endl;
return INT_MIN;
}else{
int x = arr[this->front];
this->front = (this->front + 1) % SIZE;
if(this->rear == this->front) tag = false;
return x;
}
}
